Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-12-22 Origin: Site








In the world of batteries, whether they are for electric vehicles, power tools, or energy storage systems, one term that often comes up is C rating. But what does it mean? And why is it so important to understand when choosing the right battery for your application? If you've ever wondered about the significance of a battery's C rating or found yourself confused when browsing specifications, you're not alone. This article will help you decode this crucial parameter and understand how it affects battery performance, lifespan, and safety.
In this post, we'll break down the concept of C rating, explain how to calculate it, explore different types, and show you how it affects the performance of batteries in various applications. By the end, you'll be equipped with the knowledge to make more informed decisions when selecting batteries for your needs, whether it's for high-performance applications or long-lasting energy storage.
C rating is a measurement that defines how quickly a battery can be charged or discharged relative to its capacity.
A high C rating allows for faster charging and discharging, but it may reduce the battery's lifespan and affect safety.
Different battery applications require different C ratings, with high-powered tools and electric vehicles needing higher C ratings, while energy storage systems typically require lower ones.
Understanding C rating can help you select the right battery for your specific needs, ensuring optimal performance, lifespan, and safety.
The C rating (or C rate) of a battery is a standard measure used to define the rate at which a battery is discharged or charged relative to its maximum capacity. For example, if a battery has a capacity of 100Ah, a C rating of 1C means it can discharge 100A for one hour.
Mathematically, it can be calculated as:

A 100Ah battery with a C rating of 1C can discharge at 100A for one hour.
If the battery has a C rating of 2C, it can discharge 200A for half an hour.
For a battery with a capacity of 100Ah and a C rating of 2C:
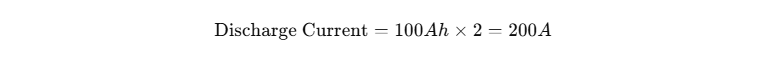
The battery will discharge at 200A for half an hour.
Batteries can have multiple types of C ratings, with the two most common being continuous C rating and pulse C rating.
Continuous C rating:
This defines the maximum rate at which a battery can discharge or charge continuously without damaging itself.
For example, a 100Ah battery with a continuous C rating of 1C can discharge at 100A for an extended period of time without overheating or degrading.
Pulse or Peak C rating:
This defines the maximum discharge or charge rate that a battery can handle in short bursts, usually lasting only a few seconds or minutes.
Pulse C rating is especially important for applications that require high power output over short durations, such as in power tools or electric vehicles.
Continuous C rating: A 100Ah battery with a 1C continuous rating can provide 100A continuously.
Pulse C rating: A 100Ah battery with a 3C pulse rating can provide up to 300A for a short burst.
The C rating has a direct impact on battery performance, lifespan, and safety. Batteries with a high C rating can deliver more power more quickly, but this comes at a cost.
A higher C rating allows for faster charging and discharging, which is essential for high-performance applications such as electric vehicles (EVs) or power tools.
A lower C rating, on the other hand, is typically preferred for energy storage systems that need to provide a consistent power output over a longer period.
Discharging a battery at a higher C rating increases the strain on the battery, which can shorten its lifespan. Excessive discharging can also result in overheating, leading to degradation of internal components.
Batteries with lower C ratings tend to last longer because they operate within their safe discharge limits.
Operating a battery above its specified C rating can cause excessive heat buildup, leading to thermal runaway or even a fire in extreme cases.
To maintain safe operation, it's essential to select a battery with an appropriate C rating for your specific application.
The C rating varies depending on the type of battery and its intended application. Here's a look at typical C ratings for common battery types:
| Battery Type | Typical C Rating | Application |
|---|---|---|
| LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) | 0.5C to 1C | Energy storage, solar power backup, UPS systems |
| NCM (Nickel Cobalt Manganese) | 1C to 3C | Electric vehicles, power tools, drones |
| LTO (Lithium Titanate) | 5C to 10C | High-power applications like fast charging stations, buses |
| Lead-acid batteries | 0.1C to 0.3C | Backup systems, low power applications |
Key Takeaways:
LiFePO4 batteries typically have a C rating of 0.5C to 1C, making them ideal for energy storage systems where moderate discharge rates are sufficient.
NCM batteries, with C ratings of 1C to 3C, are commonly used in electric vehicles where higher power output is needed for acceleration and climbing.
LTO batteries can achieve C ratings of up to 10C, making them suitable for applications that require very high power output over short durations, such as in buses or high-speed charging stations.
When you're shopping for batteries, particularly in B2B settings or for technical applications, understanding how to read the C rating is crucial.
Continuous Discharge C Rating: Indicates the safe discharge rate the battery can sustain over long periods without overheating.
Peak or Pulse Discharge C Rating: Represents the maximum burst discharge rate, typically for short periods.
Charging C Rating: Similar to the discharge C rating, this shows the maximum charging current that can be applied safely.
Always check both the continuous and pulse ratings when evaluating a battery, as this will give you a complete understanding of its capabilities.
For battery manufacturers, understanding and accurately specifying the C rating is critical for both performance and customer safety. Properly rated batteries ensure:
Reliable performance: By accurately specifying the C rating, manufacturers can ensure that their batteries meet the necessary power demands of their intended applications.
Safety compliance: Accurate C ratings help to prevent accidents such as overheating or fire, which can occur if batteries are discharged or charged too quickly.
Extended lifespan: By not exceeding the rated C rating, manufacturers can help ensure that their batteries last as long as possible, giving customers better value.
Understanding the C rating of a battery is essential for selecting the right battery for your needs. Whether you're using it in an electric vehicle, for energy storage, or for power tools, knowing the C rating will help you choose a battery that offers optimal performance, safety, and longevity. By paying attention to this critical specification, you'll be able to make more informed decisions and ensure that your battery operates within its safe limits.
Continuous C rating refers to the constant discharge or charge rate a battery can handle, while pulse C rating refers to the maximum discharge or charge rate for short bursts of power.
While it may seem tempting, using a battery above its rated C rating can lead to overheating, shorten its lifespan, and pose safety risks. Always follow the manufacturer's specifications.
If your application requires high power output for extended periods, look for a battery with a higher continuous C rating. For applications that require short bursts of power, a high pulse C rating will be more suitable.