Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-01 Origin: Site








When you look at lithium iron phosphate batteries, you see four main lifepo4 battery cell types. These are cylindrical, prismatic, pouch, and large-format. Each lifepo4 battery cell type has its own design. They are made for different uses. Cylindrical lifepo4 battery cells are good for power banks and flashlights. Prismatic lifepo4 battery cells are used in energy storage systems and electric vehicles. Pouch lifepo4 battery cells are found in smartphones and drones. Large-format lifepo4 battery cells are used for big jobs. The table below shows where each type is used:
LiFePO4 Cell Type | Description & Characteristics | Most Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
Cylindrical | Round shape, even heat, mature production | Power banks, drones, flashlights, tools |
Prismatic | Square, high capacity, stable packs | Energy storage, low-speed vehicles, AGVs |
Pouch | Lightweight, customizable, bulges on failure | Smartphones, drones, wearables, cars |
These lifepo4 battery cell types help you pick the right lifepo4 battery for your project. Lithium iron phosphate makes lifepo4 battery cells last a long time and keeps them safe. You can find lifepo4 battery cells in many lifepo4 batteries today.
LiFePO4 batteries have four main cell types. These are cylindrical, prismatic, pouch, and large-format. Each type has a different shape and use.
Cylindrical cells are strong and safe. They work well in tools and power banks. Prismatic cells save space and store more energy. They are good for electric vehicles and storage.
Pouch cells are light and bend easily. They are great for drones and wearables. But they need careful handling. Large-format cells give lots of power. They are used in big machines like forklifts and trucks.
Battery grade and current rating are important. Grade A cells last the longest and are safest. Pick a C-rate that fits your device's needs. This keeps batteries safe and working well.
LiFePO4 batteries last a long time. They give steady power and are very safe. This makes them a smart choice for many things. You can use them in small gadgets or big machines.
There are four main designs of lifepo4 battery cells. Each type has its own shape and is made for certain jobs. Let's see what makes each one different.
Cylindrical cells are used in tools, power banks, and electric vehicles. They have a round steel shell and a steel cap. Inside, there are positive and negative electrodes, a separator, electrolyte, a gasket, and a safety valve. The electrodes are wound in a spiral, which gives the cell its round shape.
Cylindrical cells come in sizes like 18650, 26650, and 32700.
They handle pressure well and cool down easily because of air gaps.
You can put them together in rows and columns to make battery packs.
The steel shell makes them heavier but keeps them safe.
These cells cost less because they are easy to make.
Here is a table with the main features:
Structural Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
Shape and Shell | Round steel shell and cap for strong safety |
Internal Components | Positive/negative electrodes, separator, electrolyte, gasket, safety valve |
Standard Sizes | 18650, 26650, 32700, and more |
Electrode Structure | Spiral-wound inside the shell |
Heat Dissipation | Good, because of air gaps |
Space Utilization | Lower, due to air gaps |
Weight | Heavier from the steel shell |
Manufacturing Cost | Lower, since production is mature |
Damage Tolerance | One cell failing rarely ruins the whole pack |
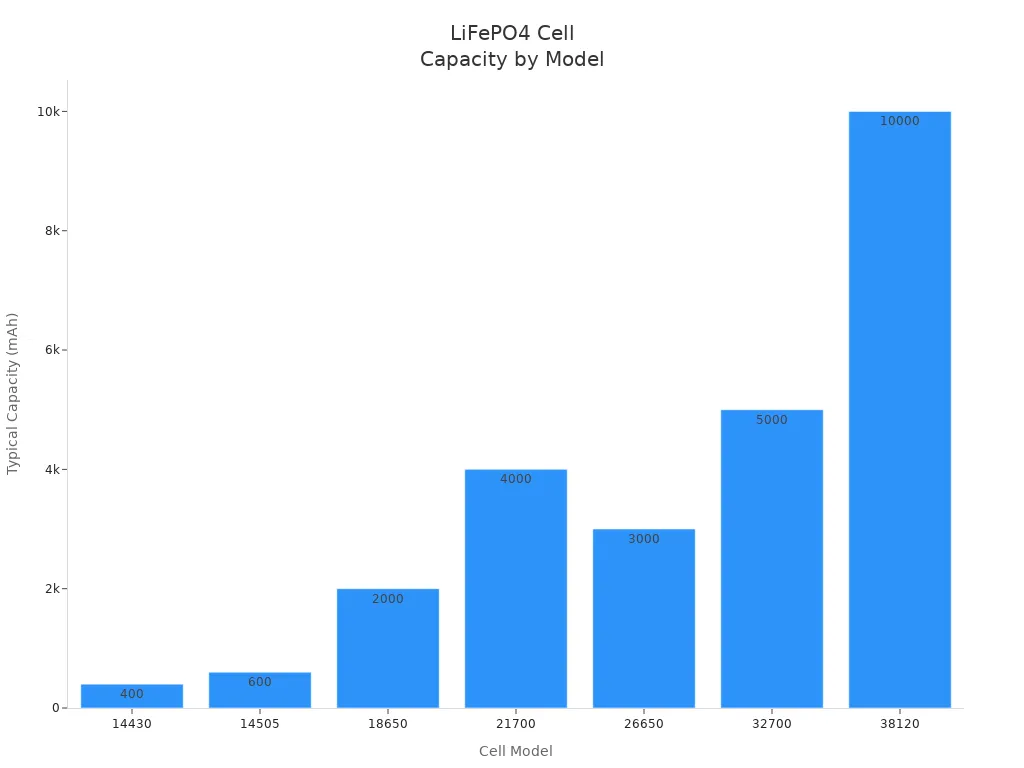
You can see the usual sizes and capacities in this table:
Cell Model | Diameter (mm) | Length (mm) | Typical Capacity (mAh) | Nominal Voltage (V) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
14430 | ~14 | ~30 | ~400 | 3.2–3.3 | Small devices |
14505 | ~14.5 | ~50 | ~600 | 3.2–3.3 | Standard AA size |
18650 | 18 | 65 | 2000–3500 | 3.2–3.3 | EVs, power tools |
21700 | 21 | 70 | 4000–5000 | 3.2–3.3 | EVs, energy storage |
26650 | 26 | 65 | 3000–6000 | 3.2–3.3 | Larger power tools |
32700 | 32 | 70 | 5000–8000 | 3.2–3.3 | Industrial storage |
38120 | 38 | 120 | 10000–12000 | 3.2–3.3 | Large-scale storage |
Tip: If your device needs good cooling and easy swapping, pick a cylindrical cell.
Prismatic lifepo4 battery cells are flat and shaped like rectangles. They use layers inside a hard, flat case. This shape lets you fit more energy in a small space. Prismatic cells are used in electric vehicles, energy storage, and robots.
Prismatic cells fill almost all the space in a battery pack, so each cell holds more energy.
You need fewer cells for big packs, which makes building easier.
The flat shape can make cooling harder, so you must plan for it.
The case is not as strong as steel, so you must protect it from bumps.
Here is a table comparing prismatic and cylindrical cells:
Feature | Cylindrical LiFePO4 Cells | Prismatic LiFePO4 Cells |
|---|---|---|
Shape | Round | Rectangular (flat) |
Casing | Steel shell | Hard, flat casing |
Internal Design | Spiral-wound electrodes | Layered electrodes |
Space Utilization | Lower (gaps between cells) | Nearly 100% |
Thermal Management | Good | More challenging |
Mechanical Stability | Very robust | Less robust |
Capacity per Cell | Lower | Higher |
Manufacturing | Standard sizes, low cost | Custom sizes, higher cost |
You find prismatic lifepo4 battery cells in:
Electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs)
Solar and wind energy storage systems
Off-grid backup power
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs)
Note: Prismatic cells are best when you want high capacity and to save space in your battery pack.
Pouch lifepo4 battery cells use a thin, bendy pouch instead of a hard case. This makes them very light and easy to shape. You see pouch cells in phones, drones, wearables, and some electric cars.
The pouch can be as thin as 4mm, so it fits in slim devices.
It weighs up to 40% less than a cylindrical cell and 20% less than a prismatic cell.
You can make special shapes for unique devices.
The pouch swells or cracks if it fails, which helps release energy safely.
It needs careful handling because the pouch is not as strong as metal.
Here is a table showing how pouch cells compare to other types:
Feature | Pouch LiFePO4 Cells | Prismatic/Cylindrical Cells |
|---|---|---|
Casing | Flexible, soft pouch | Rigid metal case |
Weight | Much lighter | Heavier |
Profile Thickness | As thin as 4mm | Bulkier |
Space Efficiency | Very high | Lower |
Mechanical Strength | Moderate | Very high |
Thermal Safety | Swells/cracks to release energy | Risk of explosion |
Heat Dissipation | Effective | Good |
Application Focus | Wearables, drones, medical devices | Heavy-duty uses |
Pouch cells give you more design choices and higher energy for their size. They are best for devices where space and weight matter most. But they need extra care to avoid damage and getting too hot.
Tip: Pick pouch lifepo4 battery cells for wearables, drones, or medical devices where every gram and millimeter is important.
Large-format lifepo4 battery cells are made for big machines and systems. You find them in factories and businesses, like forklifts, trucks, ships, and backup power.
These cells have high capacity, from 45.6 Ah up to 200 Ah.
They work with voltages from 12 V to 48 V.
You can use them in systems that grow bigger as needed.
They are used in electric vehicles, telecom, and boats.
Common uses include:
Industrial vehicles like forklifts and trucks
Commercial electric vehicles such as shuttles and golf carts
Backup power for telecom equipment and UPS systems
Robotics and warehouse automation
Marine propulsion for ferries and ships
Airport ground vehicles
Large-format lifepo4 battery cells help you build strong, reliable systems for heavy work.
Now you know the main types of lifepo4 battery cells. Each type is made for a different job, from small gadgets to big machines. When you pick a lifepo4 battery, think about the shape, size, and what you need it for. Lithium iron phosphate chemistry gives all these types long life and safety, making them a great choice for many batteries.
Each lifepo4 battery cell type has a different look and build. Cylindrical cells are round with a metal shell. Prismatic cells have a flat, box-like case. Pouch cells use a soft, bendy pouch. Large-format cells are bigger versions for tough jobs. The table below lists the main design features:
Design Aspect | Cylindrical Cells | Prismatic Cells | Pouch Cells |
|---|---|---|---|
Shape | Tubular, metal casing | Rectangular, flat casing | Flexible, flat pouch |
Structure | Rolled electrodes | Layered electrodes | Layered in soft pouch |
Space Efficiency | Stackable, some gaps | Very space-efficient | Fits odd shapes |
Flexibility | Fixed shape | Rigid | Highly flexible |
Weight | Moderate | Moderate | Very light |
Cost | Affordable | Higher | Cost-effective |
Tip: If you need a lifepo4 battery for small spaces, try pouch or prismatic cells.
Different lifepo4 battery cell types work in different ways. Lithium iron phosphate helps all types last long and stay safe. Most lifepo4 battery cells can be charged over 4000 times. Cylindrical cells cool well and give steady power. Prismatic cells hold more energy and give strong output. Pouch cells store lots of energy in a small space but need gentle care. Large-format cells power big machines and hold lots of energy.
Cylindrical cells are good for tools and electric vehicles. They stay cool and last a long time.
Prismatic cells are used in big battery packs. They give lots of power and save space.
Pouch cells are best for thin devices. They store more energy for their size.
Large-format cells are used in forklifts, boats, and backup systems.
It is important to know the good and bad points of each lifepo4 battery cell type.
Cylindrical Cells
Lasts long, safe, easy to make, strong shell
Heavy, not as space-saving
Prismatic Cells
Holds lots of energy, saves space, easy to stack
Costs more, case is not as strong
Pouch Cells
Light, bendy, fits many shapes
Needs gentle care, can swell if damaged
Large-Format Cells
Very high capacity, great for big jobs
Heavy, needs strong support
Note: All lithium iron phosphate batteries are safe, last long, and give steady power. They might cost more and take up more room than other types.
Lifepo4 battery cells are used in many things. Each lifepo4 battery cell type is made for different jobs.
Cylindrical: Power tools, electric bikes, flashlights, solar power systems
Prismatic: Electric cars, home energy storage, golf carts, AGVs, residential lifepo4 battery
Pouch: Drones, wearables, medical devices, some electric vehicles
Large-format: Forklifts, trucks, boats, backup power, industrial machines
Pick your lifepo4 battery cell type based on your space, power, and safety needs. Lithium iron phosphate batteries are best when you want long life and safe use.
When you pick a lifepo4 battery, you will see three quality grades. These are Grade A, Grade B, and Grade C. Each grade shows how well the cell works and how long it lasts.
Grade A
Passes all tests and rules.
No swelling or damage at all.
Made with top materials and works very well.
Size and power are always the same.
Used in electric cars, solar storage, and medical gear.
Grade B
Works at about 80–90% as well as Grade A.
Might be a little different in size or power.
Has a few more defects than Grade A.
Good for backup power, e-bikes, and gadgets.
Grade C
Not as good in any way.
Can swell or lose power fast.
Often comes from old or stored stock.
Used in toys, cheap electronics, or for testing.
Quality Grade | Performance | Lifespan | Consistency | Safety Standards | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Grade A | Highest | Longest | Very high | Rigorous | EVs, solar, medical |
Grade B | Good | Moderate | Some | Adequate | E-bikes, backup |
Grade C | Lowest | Shortest | Low | Basic | Toys, prototyping |
Tip: Grade A lifepo4 battery cells are safest and last the longest.
Current ratings tell you how fast a lifepo4 battery can charge or give power. These ratings use C-rates, like 1C, 2C, or 5C. A 1C rating means the battery gives all its power in one hour. A 2C rating means it does this in half an hour.
Low C-rate (1C–2C):
Good for slow, steady use. You find these in home storage and UPS.
Medium C-rate (3C–5C):
Gives more power in less time. Used in electric cars and power tools.
High C-rate (6C–10C+):
Gives quick bursts of energy. Needed for racing cars, drones, and pro tools.
Current Rating (C) | Typical Use | Main Feature |
|---|---|---|
1C | Energy storage | Long, steady power |
2C / 3C | Power tools, e-bikes | More power, faster output |
5C+ | Racing, drones | High power, short bursts |
Note: The right C-rate keeps your lifepo4 battery safe and working longer.
You must match the lifepo4 battery grade and C-rate to your project. Grade A is best for important jobs like electric cars or solar storage. Grade B is good for backup power or e-bikes. Grade C is fine for toys or testing. Pick a C-rate that fits your device. High-power tools need higher C-rates. Home storage needs lower C-rates for longer use.
Figure out your device's power needs before buying.
Use a battery management system (BMS) to keep cells safe.
Do not use high C-rate batteries for low-power jobs. It costs more and does not help.
Never use low C-rate batteries for high-power tools. This can cause overheating and early failure.
Always check the grade and C-rate when picking a lifepo4 battery. This helps you get the best safety and performance.
The main types of lifepo4 battery cells look very different. Each type has its own size and shape. They also pack energy in different ways. Some types use space better than others. The table below helps you see the differences:
Cell Type | Structure & Packaging | Typical Size (mm) | Energy Density & Packaging Efficiency | Advantages & Disadvantages Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Cylindrical | Hard steel shell | Diameter: 18, Height: 65 | Lower system energy density; heat dissipation challenges | Mature technology, high reliability, low cost; but lower packaging efficiency and heat dissipation issues after grouping |
Prismatic | Rectangular aluminum shell | Thickness: 30, Width: 135, Length: 220+ | Higher single cell energy density; better system grouping efficiency | Simple structure, high packaging reliability; variability in models and lifespan concerns |
Pouch (Soft Pack) | Flexible aluminum plastic film | Variable shapes (triangular, square, circular, arc) | Highest energy density; smallest internal pack size | High energy density and cycle life; higher cost, lower production efficiency, and yield |
Pouch cells use space the best. Prismatic cells also fit well in packs. Cylindrical cells are strong but take up more room.
If you design your battery pack well, you can fit up to 20% more cells. This means how you build the pack is very important.
Safety and durability are important for lifepo4 battery cells. All types are safe and last a long time. The table below shows the main safety and durability features:
Feature Category | Details |
|---|---|
Durability Metrics | Long cycle life, high energy density, stable voltage output, good for long-term use |
Safety Features | Thermal stability, reduced risk of thermal runaway, built-in vents, BMS monitoring |
Application Suitability | Electric vehicles, solar storage, backup power, portable power banks |
Key Factors | Capacity, voltage, size, weight, cycle life, cost-effectiveness |
Small cells like 18650 stay cooler and are safer. Bigger cells like 26650 can get hotter and need better cooling. All lifepo4 battery cells follow strict safety rules. You should always use a battery management system (BMS) for best safety.
The price and how easy it is to find lifepo4 battery cells depends on the type and where you live. The table below shows average prices and trends:
Battery Cell Type / Application | Average Cost (2025) | Market Availability and Trends |
|---|---|---|
LiFePO4 (LFP) Cells in China | Below $60 per kWh, around $44 per kWh | Large-scale production, Asia leads, prices dropping |
Global Average Lithium Battery Price | $85 to $100 per kWh | Prices falling, Asia lowest, Europe/US higher |
Industrial/Tools Batteries (2 to 12 Ah) | $110 to $335 | Prices dropping, supply-demand affects cost |
Solar and Energy Storage Systems (~10 kWh) | $6,000 to $12,000 | High demand, price depends on region and supply chain |
Asia has the cheapest prices and lots of supply. Europe and North America cost more because of higher wages and rules. Prices are going down as more factories make these cells.
You should pick the lifepo4 battery cell type that fits your needs:
Cylindrical cells: Good for power tools, e-bikes, and small devices. They are safe and not expensive.
Prismatic cells: Great for electric cars and home batteries. They save space and hold more energy.
Pouch cells: Best for drones, wearables, and thin gadgets. They fit odd shapes and are very light.
Large-format cells: Used in forklifts, trucks, and backup power. They give lots of energy for big jobs.
Studies show lifepo4 battery cells are best for electric cars, home storage, and portable electronics. They last a long time, are safe, and cost less than other types. Most people choose them for their long life and steady power.
You now know the main types of LiFePO4 battery cells. Each type has its own strengths:
Cylindrical: Strong and safe for tools or bikes.
Prismatic: Space-saving for cars or home storage.
Pouch: Light and flexible for drones or wearables.
Large-format: High power for big machines.
Always check the cell grade and current rating. These details help you pick the safest and longest-lasting battery for your project.
LiFePO4 cells use a stable chemistry. They resist overheating and fire. You get strong thermal stability. They rarely explode or catch fire. This makes them a top choice for safety.
First, check your device's size and power needs. Use cylindrical cells for tools. Pick prismatic for cars or storage. Choose pouch for light gadgets. Large-format cells work best for heavy machines.
You should not mix grades. Grade A, B, and C cells have different performance and lifespan. Mixing them can cause uneven charging, faster wear, or safety risks.
Most LiFePO4 cells last 2,000 to 5,000 cycles. You can use them for 5 to 10 years. Their long life makes them great for solar, EVs, and backup power.